6.8 Sex hormone responsive conditions
| First line drugs | Second line drugs | Specialist drugs | Secondary care drugs |
Traffic light status (TLS) explained:
- Green: Routine prescribing within licensed indication
- Amber 1: specialist recommendation followed by GP initiation and continuation
- Amber 2: specialist or GP initiation in line with local guideline after 1st line failure followed by GP continuation
- Amber 3: specialist initiation and stabilisation followed by GP continuation
- Amber SCG: specialist initiation and stabilisation followed by GP continuation in line with an agreed shared care guideline
- Red: Hospital or specialist prescribing only
Sex hormones
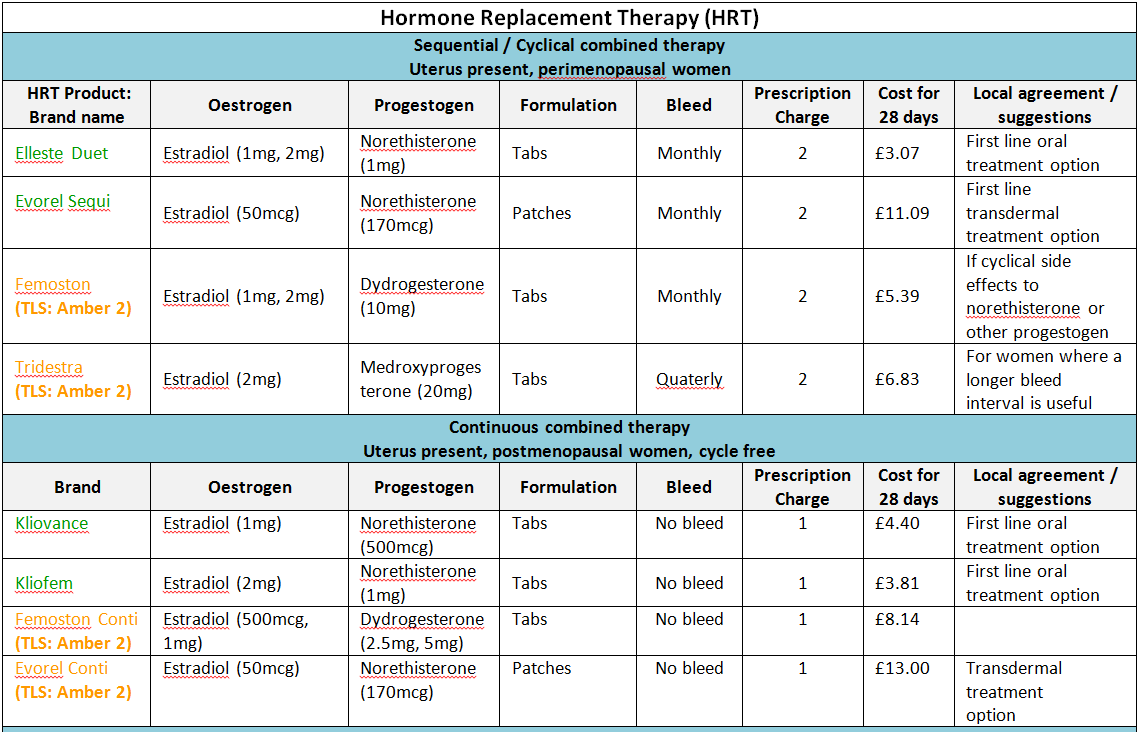
Oestrogens and HRT
The benefits and risks of Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT).
Short-term treatment of menopausal symptoms
- The benefits of short-term treatment (with the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration) are still considered to outweigh the risks for the majority of women. Women should be fully informed and reviewed annually.
Prevention of osteoporosis
- HRT should not be considered first-line therapy for the long-term prevention of osteoporosis in women >50 and at an increased risk of fractures.
Women with premature menopause
- HRT may be used in younger women who have experienced a premature menopause (due to ovarian failure, surgery or other causes) for treating their menopausal symptoms and preventing osteoporosis until the age of 50 years. After this age, therapy for preventing osteoporosis should be reviewed and HRT considered a second-line choice.
Healthy women without symptoms
- The risk: benefit of HRT is generally unfavourable.
Benefits
- Control of menopausal symptoms – such as hot flushes, night sweats and vaginal dryness.
- Reduced number of colorectal cancer cases
- Osteoporosis – the use of HRT for the prevention of osteoporosis is well established.
The Risks of Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT).
Notes:
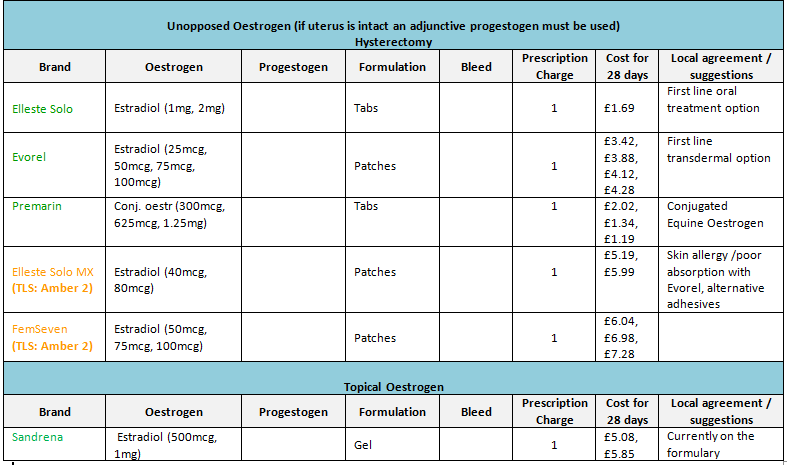
- Oral preparations, which are cheaper and widely used, tend to be first line therapy (DTB November 96). Patches should only be given if there is a need to bypass liver metabolism and patient preference.
- For more comprehensive information of formulary products see ‘Joint Formulary – Hormone Replacement Therapy’ (Section 6.4.1.2).
- Prior to prescribing, patients may wish to know that conjugated oestrogens (Premarin®, Prempak-C® and Premique®) are derived from urine of farmed horses.
- NB: Where patches are included in the formulary their strengths are expressed as dose delivered per 24 hours.
6.8.1 Female sex hormone responsive conditions
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
Others:
Raloxifene®
- Tablets 60mg
Notes:
- Raloxifene is licensed for the treatment and prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis;
- Unlike HRT therapy, raloxifene does not reduce menopausal vasomotor symptoms.
- Use as per NICE TA160: Raloxifene for the primary prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women (October 2008; Last updated Feb 2018)
- Use as per NICE TA161: Raloxifene and teriparatide for the secondary prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women (Oct 2008; Last updated Feb 2018)
Ethinylestradiol (Amber 1)
- Tablets 2 micrograms, 10 micrograms, 50 micrograms, 1mg
Notes:
- Tablets 10 micrograms, 50 micrograms, 1mg, 2 microgram unlicensed special.
- Licensed for short term treatment of oestrogen deficiency, female hypogonadism and menstrual disorders.
- Ethinylestradiol tablets are very expensive consider using oestradiol where clinically appropriate as a more cost effective option.
- Ethinylestradiol is included for the specialist treatment of hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia.
Progestogens
Medroxyprogesterone acetate
- Tablets 5mg, 10mg
- Endometriosis, dysfunctional uterine bleeding
Medroxyprogesterone acetate
- Tablets 5mg, 10mg
- Treatment of infertility
Norethisterone
- Tablets 5mg
- 5mg preparation is not licensed for HRT.
Progesterone
- Pessaries 200mg, 400mg (Cyclogest)
- Vaginal gel 90mg per application (Crinone)
- Injection 50mg in 1ml, 100mg in 2ml (Gestone)
- All specialist use only for the treatment of infertility
Ulipristal Acetate
Drug Safety Update. August 2018. Esmya (ulipristal acetate) and risk of serious liver injury: new restrictions to use and requirements for liver function monitoring before, during, and after treatment.
Advice for healthcare professionals:
Restricted indication and new contraindication
• Esmya is now indicated for:
o the intermittent treatment of moderate to severe symptoms of uterine fibroids in women of reproductive age who are not eligible for surgery
o one treatment course of pre-operative treatment of moderate to severe symptoms of uterine fibroids in adult women of reproductive age
• Esmya treatment is to be initiated and supervised by physicians experienced in the diagnosis and treatment of uterine fibroids
• Esmya is contraindicated in women with underlying liver disorders
Liver function monitoring
• before initiation of each treatment course: perform liver function tests; do not initiate Esmya in women with baseline alanine transaminase (ALT) or aspartate aminotransferase (AST) more than 2-times the upper limit of normal [ULN]
• during the first 2 treatment courses: perform liver function tests every month
• for further treatment courses: perform liver function tests once before each new course and when clinically indicated
• at the end of each treatment course: perform liver function tests after 2–4 weeks
• stop Esmya treatment and closely monitor women with ALT or AST more than 3-times ULN; consider the need for specialist hepatology referral
Discuss the risk of liver damage with Esmya with women and report any suspected adverse drug reactions
• before initiation of Esmya, discuss with women the rare risk of liver damage and need for liver function testing before, during, and after each treatment course
• advise women to seek urgent medical attention if they develop any symptoms or signs of liver injury (such as tiredness, yellowing of the skin, darkening of the urine, nausea and vomiting)
• pharmacists should provide the new patient card to women when dispensing Esmya; copies of this card are included in the letter sent to healthcare professionals and are available online
• report any suspected adverse drug reactions to Esmya on a Yellow Card without delay
Ulipristal acetate
- Esmya® Tablets 5mg
6.8.1a Anti-oestrogens
Ovulation stimulants
Clomifene citrate®
- Clomid® 50 mg tablets
CSM Advice: The CSM has recommended that clomifene should not normally be used for longer than 6 cycles (possibly increased risk of ovarian cancer)
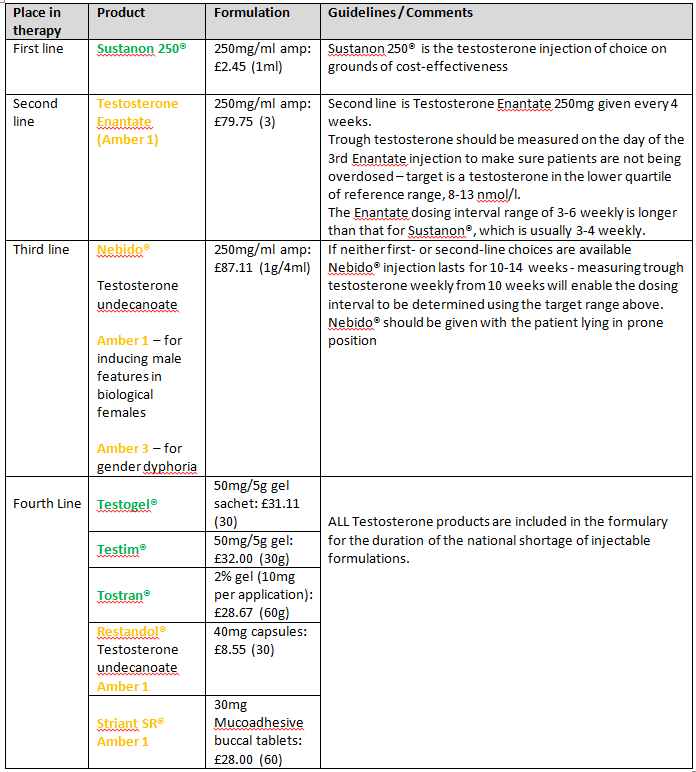
6.8.2 Male sex hormone responsive conditions
Testosterone
Notes:
- Prescribers must seek prior approval from the Individual Funding Request (IFR) panel for all testosterone products used for female hypoactive sexual desire disorder.
- NHS England Interim Gender Dysphoria Protocol and Service Guideline (pdf)
- Good practice guidelines for the assessment and treatment of adults with gender dysphoria (October 2013)
- Three gel products are included to provide for patient preference.
- Sustanon® injection may be used for androgen deficiency.
Gender Specialist Clinic - London (Charing Cross)
Lead Clinician: Dr James Barrett
West London Mental Health Trust
Gender Identity Clinic
179 – 183 Fulham Palace Road
London W6 8QZ
6.8.4 Male sex hormone antagonism
Anti-Androgens
Cyproterone acetate
- Tablets 50mg
Traffic light status (TLS) explained:
- Green: Routine prescribing within licensed indication
- Amber 1: specialist recommendation followed by GP initiation and continuation
- Amber 2: specialist or GP initiation in line with local guideline after 1st line failure followed by GP continuation
- Amber 3: specialist initiation and stabilisation followed by GP continuation
- Amber SCG: specialist initiation and stabilisation followed by GP continuation in line with an agreed shared care guideline
- Red: Hospital or specialist prescribing only
Return to Chapter: 6. Endocrine System
Last updated by: Dupe Fagbenro on 02-04-2019 12:24