13.3 Inflammatory skin conditions
| First line drugs | Second line drugs | Specialist drugs | Secondary care drugs |
Traffic light status explained:
- Green: Routine prescribing within licensed indication
- Amber 1: specialist recommendation followed by GP initiation and continuation
- Amber 2: specialist or GP initiation in line with local guideline after 1st line failure followed by GP continuation
- Amber 3: specialist initiation and stabilisation followed by GP continuation
- Amber SCG: specialist initiation and stabilisation followed by GP continuation in line with an agreed shared care guideline
- Red: Hospital or specialist prescribing only
13.3.1 Eczema and Psoriasis
Infected Eczema - Treatment guidance
Infected Eczema Treatment Guidelines (May 2017)
Eczema - Treatment guidance as follows:
Mild eczema
- Emollients (see 13.1 Dry and scaling skin disorders)
- Important in the treatment of eczema as the skin is usually dry and lacks the natural oily protective barrier. They also soften and smooth the skin and improve itching that may be present. They must be used frequently, at least twice daily, on all areas of the skin even where there is no visible sign of eczema. They should be used every 2 hours when the condition is florid.
- Mild potency topical steroid (can be used on all areas including face and neck) (see section Corticosteroids (topical))
- Useful where there is an inflammatory component to the disease and to reduce itching. The strength and type of steroid prescribed depends on the age of the patient, the site affected, the severity of the eczema and whether or not infection is present.
Moderate eczema
- Emollients (see 13.1 Dry and scaling skin disorders)
- Moderate potency topical steroid (use for 7-14 day bursts only for flares in axillae and groins, and for 3-5 day bursts only for flares on face and neck) (see section Corticosteroids (topical))
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors (see section Calcineurin inhibitors and related drugs)
- Other treatments applying a dry tubular bandage over topical treatments can be helpful when proving difficult to control. Seek advice from dermatology specialist nurses.
- Bandages / garments
- Phototherapy
- Systemic therapy
Severe eczema
- Emollients (see 13.1 Dry and scaling skin disorders)
- Potent topical steroid for 7-14 day bursts (do not use on face, neck, axillae, groins, or elbow and knee flexures). Do not prescribe potent topical steroids in children younger than 12 months, or very potent topical steroids younger than 16 years in primary care without specialist dermatological advice. (see section Corticosteroids (topical))
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors (see section Calcineurin inhibitors and related drugs)
- Other treatments applying a dry tubular bandage over topical treatments or using a wet or paste bandage on severe eczema can be helpful when proving difficult to control. Seek advice from dermatology specialist nurses.
- Bandages / garments
- Phototherapy
- Systemic therapy
Corticosteroids (Topical)
Notes:
NICE TA81: Frequency of application of topical corticosteroids for atopic eczema (Aug 2004)
Patients should be initiated on the highest potency topical corticosteroid that is clinically required and then stepped down. The patient may be stepped down to a lower potency steroid or the frequency of use of a higher potent steroid can be reduced, for example:
Once / Twice Daily → → Alternate Days or less frequently, as necessary
By treating actively, you are more likely to get the skin condition under control.
How much corticosteroid to prescribe?
The table below shows suitable quantities of dermatological preparations to be prescribed for specific areas of the body based on a single daily application for two weeks for an adult.
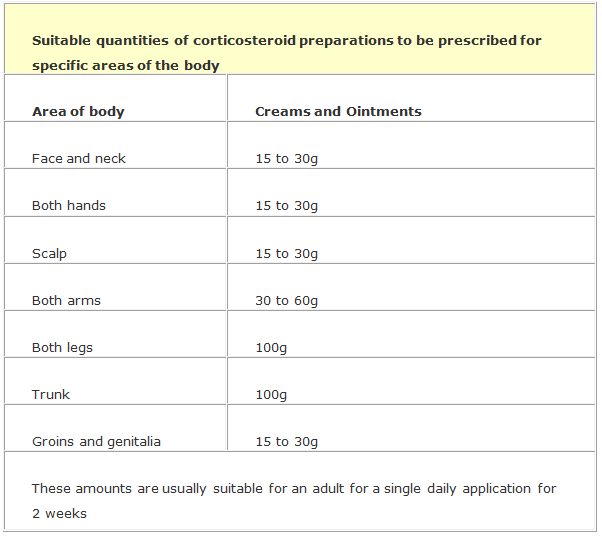
“To be spread thinly” is a cautionary warning that must legally be included on the label of topical steroid preparations - counsel patients on the correct application and ensure adequate coverage of affected areas.
The length of cream or ointment expelled from a tube may be used to specify the quantity to be applied to a given area of skin. One "fingertip unit" is sufficient to cover an area that is twice that of the flat adult palm.
For patients requiring maintenance therapy of steroids, it is important to review prescribing at least every 3 months. For patients using steroids short term, the need for repeat prescriptions should be reviewed every four weeks. The duration of therapy should be specified.
The long-term use of potent and very potent steroids should only be recommended by a dermatologist / GPwSI / nurse specialist.
Caution must be used when selecting corticosteroids for different parts of the body.
For the face and other sensitive areas of the body, a lower potency corticosteroid should be used.
Choice of Preparation:
- Ointments are preferable to creams as they have a deeper, more prolonged emollient effect and increase the penetration of steroid. They are also less likely to cause irritation (as they do not contain preservatives) and/or sensitisation to the product.
- Patients may prefer creams for application to the face and can be more suitable for moist or weeping lesions.
- Ideally, topical steroids should only be used for short periods to treat exacerbations of the disease.
- It is important to prescribe the appropriate potency of steroid according to the severity of the disease. Flare-ups can be treated with a potent or very potent steroid and then stepped down to an appropriate potency of steroid or even an emollient.
- Dilution of topical corticosteroid preparations in emollient diluents to reduce steroid potency is not advised. The shelf life of the diluted product is significantly reduced leading to unsafe use past expiry date and waste of unused preparation. Diluted preparations are significantly more expensive (often greater than £100 per 100g). It is preferable to choose a ready made product at the required steroid potency.
- Reminding patients to dispose of unwanted or out of date medicines may be worthwhile, as reuse of a microbial contaminated steroid product could be harmful.
- Topical steroids should not be used routinely on clinically infected skin, unless the infection is being treated. A short course of a suitable oral antibiotic maybe indicated.
Topical Corticosteroids with their potencies
Mild Potency
Hydrocortisone
- Ointment: 0.5%, 1%, 2.5%
- Cream: 0.5%, 1%, 2.5%
Notes:
- Hydrocortisone ointment and cream (1% or combination) is available over the counter for the treatment of allergic contact dermatitis, irritant dermatitis, insect bite reactions and mild to moderate eczema.
- It cannot be sold for application to eyes/face, anogenital region, for use in pregnancy or children under 10 years and on broken or infected skin and has a license for a maximum of one week’s duration.
Mild Potency with antimicrobial
Daktacort®
- Cream, Hydrocortisone 1%, miconazole nitrate 2%
Nystaform-HC®
- Cream, Hydrocortisone 0.5%, nystatin 100000 units, chlorhexidine hydrochloride 1% / g
Canesten HC®
- Cream, Hydrocortisone 1%, clotrimazole 1%
Moderate Potency
Betamethasone valerate
- Betnovate RD® Ointment, 0.025%
- Betnovate RD® Cream, 0.025%
Clobetasone butyrate
- Eumovate® Ointment, 0.05%
- Eumovate® Cream, 0.05%
Notes:
- Clobetasone butyrate (Eumovate®) cream can be sold over the counter for short-term symptomatic treatment and control of patches of eczema and dermatitis (but not seborrhoeic dermatitis) in adults and children over 12 years.
Moderate Potency with antimicrobial
Trimovate®
- Cream, clobetasone butyrate 0.05%, oxytetracycline 3%, nystatin 100,000 units/g
- stains clothing
Potent
Beclometasone dipropionate
- Ointment 0.025%
- Cream 0.025%
Betamethasone valerate
- Ointment 0.1%
- Cream: 0.1%
Fluocinolone acetonide
- Synalar® 0.025% ointment, 250 microgram per 1 gram
- Synalar® 0.025% cream, 250 microgram per 1 gram
Mometasone furoate 1 mg per 1 gram
- Elocon® 0.1% ointment
- Elocon® 0.1% cream
Potent with antimicrobial
Betamethasone with clioquinol
- Ointment, betamethasone as valerate 0.1% plus clioquinol 3%
- cream, betamethasone as valerate 0.1% plus clioquinol 3%
Betamethasone with salicylic acid
- Diprosalic® Ointment, betamethasone as dipropionate 0.05% plus salicylic acid 3%
Very Potent
Due to the risk of potential errors, clobetasol preparations should be prescribed by brand.
Dermovate® (Amber 1)
- Ointment, clobetasol propionate 0.05%
- Cream, clobetasol propionate 0.05%
Very Potent with antimicrobial
Clobetasol/neomycin/nystatin
- Ointment, containing Clobetasol propionate 0.05%, neomycin sulf. 0.5%, nystatin 100,000 units per g; 30g
- Cream, containing Clobetasol propionate 0.05%, neomycin sulf. 0.5%, nystatin 100,000 units per g; 30g
Scalp applications (steroidal)
Potent
Betamethasone valerate
- Betnovate® 0.1% Lotion Scalp Application
Very potent
Etrivex® (Amber 1)
- Clobetasol propionate 500 microgram/g shampoo (125mL)
Dermovate scalp application® (Amber 1)
- Clobetasol propionate 500 microgram/g (30mL)
Calcineurin Inhibitors and related drugs
Pimecrolimus ®(Amber 2)
- Elidel® Cream 1%
Tacrolimus (Amber 2)
- Protopic® Ointment 0.03%, 0.1%
Note:
- Use as per NICE TA82: Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus for atopic eczema (Aug 2004)
Oral Retinoids
Alitretinoin
- Toctino®Capsules 10mg, 30mg
Notes:
- Use according toNICE TA177: Alitretinoin for the treatment of severe chronic hand eczema (August 2009)
- Prescribing information, Patient information leaflet, SPC and Pregnancy Prevention Programmme (PPP)
Psoriasis - Treatment guidance as follows:
Local guideline: Clinical Features and treatment according to site of Psoriasis
Vitamin D and analogues
Calcipotriol
- Scalp solution, 50 micrograms/mL
- Ointment, 50 micrograms/g
Calcipotriol with betamethasone
- Dovobet® Ointment, calcipotriol 50 microgram/g + betamethasone 500 microgram/g
- Dovobet® Gel, calcipotriol 50 microgram/g + betamethasone 500 microgram/g
- Enstilar® Foam, calcipotriol 50 microgram/g + betamethasone 500 microgram/g (Amber 2)
Silkis®
- Calcitriol Ointment 3 microgram/g
(licensed for use on the face and in the flexures.)
Tars
Coal tar
- Exorex® Lotion
- Polytar® Shampoo
Notes:
- Should not be prescribed in Primary Care or at Discharge
- Advise patient to purchase, unless prescription is for long-term regular use
Coal tar with coconut oil and salicylic acid
- Capasal® Shampoo
Notes:
- Should not be prescribed in Primary Care or at Discharge
- Advise patient to purchase, unless prescription is for long-term regular use
Coal tar with salicylic acid and precipitated sulfur
- Sebco® Ointment
Notes:
- Should not be prescribed in Primary Care or at Discharge
- Advise patient to purchase, unless prescription is for long-term regular use
Antracen Derivatives
Dithranol
- Dithrocream® Cream 0.1% to 2%
Dithranol (Amber 2)
- Micanol® Cream 3%
British Association of Dermatologists accepted unlicensed dithranol preparations (extemporaneously prepared)
Dithranol 0.1% - 20%
- in emulsifying ointment with salicylic acid 2%
- in Lassar's paste
Oral retinoids for psoriasis
|
Key Pregnancy Prevention Programmme (PPP) features:
|
Acitretin
- Neotigason® Capsules 10mg, 25mg
Note:
- For hospital dermatology specialist use only
Drugs affecting the immune response (Shared care guidelines - in progress)
Azathioprine (Amber SCG)
- Tablets 25mg, 50mg
- Tablets 10mg - available on named-patient basis only
Ciclosporin (Amber SCG)
- capsules 10mg, 25mg, 50mg, 100mg
- Oral solution 100mg/mL
Note:
- Prescribe ciclosporin generically for dermatology conditions
Dimethyl fumarate
- Skilarence® Tablets gastro-resistant 30mg, 120mg
Note:
Hydroxycarbamide (Amber SCG)
- Capsule 500mg
Hydroxychloroquine (Amber SCG)
- Tablets 200mg
Methotrexate (Amber SCG)
- Tablets 2.5mg, 10mg
Mycophenolate Mofetil (Amber SCG)
- Capsules 250mg (generic)
- Tablets 500mg (generic)
- Oral suspension 1g in 5mL
Immunosuppressants
Adalimumab
- Imraldi, Injection, 40mg/0.8mL prefilled pen or prefilled syringe
- Amgevita, Injection, 20mg/0.4mL; 40mg/0.8mL prefilled pen or prefilled syringe
- Humira, Injection, 40mg/0.4mL; 80mg/0.8mL prefilled pen or prefilled syringe
- Humira, Injection, 20mg/0.2mL pre-filled syringe, 40mg/0.8mL solution in vial for first line use in paediatrics
Notes:
- To be prescribed by brand.
- First line brand in adults = Imraldi®
- Second line brand in adults = Amgevita®
- Third line brand in adults = Humira®
- Hulio and Hyrimoz are non-formulary within Milton Keynes Healthcare
- NICE TA455: Adalimumab, etanercept and ustekinumab for treating plaque psoriasis in children and young people (July 2017)
- NICE TA392: Adalimumab for treating moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa (June 2016)
- NICE TA146: Adalimumab for the treatment of adults with psoriasis (June 2008)
Brodalumab
- Kyntheum® 210mg/1.5ml solution for injection pre-filled syringes
Note:
Dupilumab
- Dupixent® 300mg/2ml solution for injection pre-filled syringes
Note:
- Use as per NICE TA534 Dupilumab for treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (Aug 2018)
Etanercept
- Enbrel® Injection, 25mg, 50mg solution in pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen
- Enbrel® Injection, 10mg powder and solvent for solution in vial for paediatric use
Notes:
- NICE TA455: Adalimumab, etanercept and ustekinumab for treating plaque psoriasis in children and young people (July 2017)
- NICE TA103: Etanercept and efalizumab for plaque psoriasis in adults (July 2006)
Guselkumab
- Tremfya® 100mg/1mL solution for injection in pre-filled syringes
Note:
Infliximab
- Injection 100mg vial
Note:
Ixekizumab
- Taltz® Solution for injection 80mg/1mL in pre-filled syringe / in pre-filled pen
Note:
- Use as per NICE TA537: Ixekizumab for treating active psoriatic arthritis after inadequate response to DMARDs (Aug 2018)
- Use as per NICE TA442: Ixekizumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (April 2017)
Secukinumab
- Cosentyx® Solution for injection, 150mg in pre-filled pen or in pre-filled syringe
Notes:
- NICE TA445: Certolizumab pegol and secukinumab for treating active psoriatic arthritis after inadequate response to DMARDs (May 2017)
- NICE TA350: Secukinumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (July 2015)
Tildrakizumab
-
Ilumetri® Solution for injection, 100mg in pre-filled syringe.
Note:
- Use as per NICE TA574: Certolizumab pegol for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (April 2019)
Ustekinumab
- Stelara® Injection, 45mg, 90mg solution in pre-filled syringe or vial
Notes:
- NICE TA455: Adalimumab, etanercept and ustekinumab for treating plaque psoriasis in children and young people (July 2017) (NHSE Commissioned; service not commissioned at MKUH)
- NICE TA340: Ustekinumab for treating active psoriatic arthritis (June 2015)
- NICE TA180: Ustekinumab for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe psoriasis
(September 2009)
Traffic light status explained:
- Green: Routine prescribing within licensed indication
- Amber 1: specialist recommendation followed by GP initiation and continuation
- Amber 2: specialist or GP initiation in line with local guideline after 1st line failure followed by GP continuation
- Amber 3: specialist initiation and stabilisation followed by GP continuation
- Amber SCG: specialist initiation and stabilisation followed by GP continuation in line with an agreed shared care guideline
- Red: Hospital or specialist prescribing only
Last updated by: Sheila Wood on 06-06-2019 14:34



